When it comes to selecting the ideal lined check valve, expertise is crucial. John Smith, a leading specialist in industrial valve technology, once stated, "Choosing the right lined check valve can prevent serious operational issues." A lined check valve is essential in various applications, especially where corrosion resistance is needed. The right choice can ensure efficiency and safety in your system.
However, not all lined check valves are created equal. Differences in materials, design, and manufacturer can significantly affect performance. For instance, some designs may lead to leaks or require frequent maintenance. It's essential to evaluate your specific needs carefully.
Consider factors like the medium you are working with. The temperatures and pressures involved also play a role in your decision. Experts recommend assessing your environment and expected performance metrics. Many users overlook these crucial details, leading to dissatisfaction. A careful selection process will ultimately save time and costs down the line. Making an informed choice on a lined check valve affects your operations deeply.
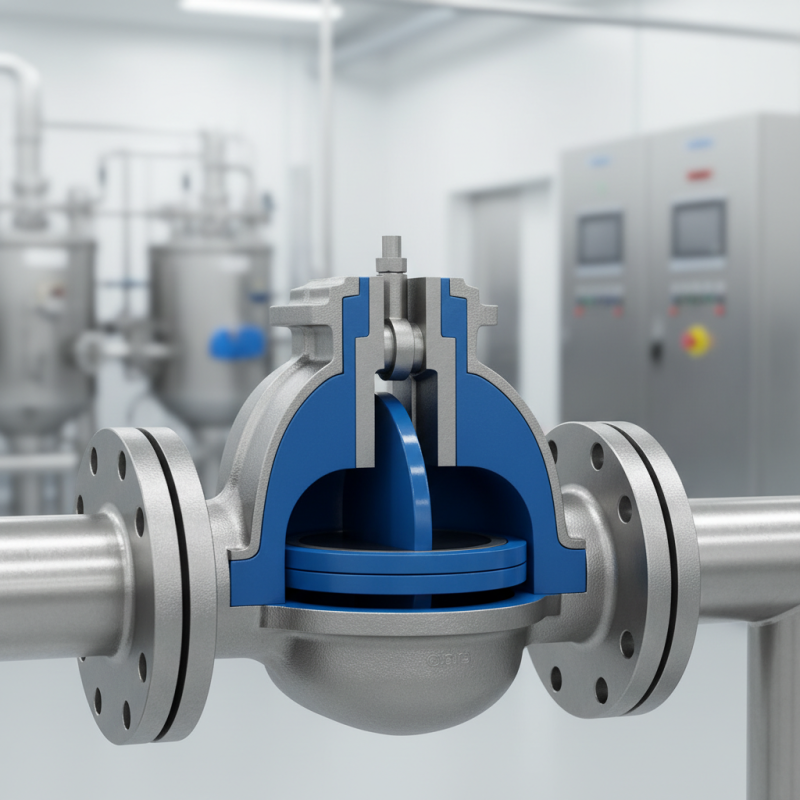

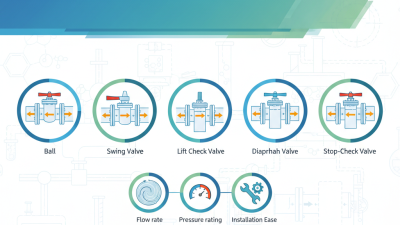
Lined check valves play a crucial role in various piping systems. They prevent backflow, ensuring that fluids flow in one direction. This functionality protects equipment and maintains system integrity. However, choosing the right valve is not always straightforward.
Consider the material of the lining. It must be compatible with the fluid type. A mismatch can lead to inefficiency or failure. Additionally, the pressure rating and temperature limits are vital. High-pressure systems need valves designed to withstand strain. Keep in mind that oversizing a valve may lead to turbulence, while undersizing may cause pressure drops.
The design of the valve also matters. A simple design can be easier to maintain. However, complex designs might offer better performance in specialized applications. Evaluate your specific needs carefully. Sometimes, an over-engineered product can be more trouble than it's worth. Check reviews and seek advice from professionals. Their insights could highlight potential pitfalls in your selection process.
Lined check valves are essential in various industries. Their primary function is to prevent backflow. This is crucial in applications like chemical processing, water treatment, and oil refining. Choosing the right valve could be challenging, but understanding key applications helps.
In chemical processing, these valves protect against corrosion. They can handle aggressive substances, ensuring safety. For water treatment, lined check valves maintain flow direction and prevent contamination. They are vital in keeping systems clean and functional.
In oil refining, they prevent backpressure. This keeps the process smooth and efficient. However, miscalculating the valve size can lead to failures. It’s important to assess pressure requirements carefully.
When selecting a lined check valve, evaluating the materials and construction is crucial. Many applications demand resistance to chemicals and high temperatures. According to a recent industry report, over 40% of valve failures occur due to material incompatibility. This highlights the need for careful material selection.
Common materials for lined check valves include PTFE, FEP, and PFA. Each has unique properties. For instance, PTFE offers excellent chemical resistance but can suffer at high temperatures. FEP, while also resistant, may not handle certain aggressive chemicals as well as PTFE. A wrong choice can lead to leaks and costly downtime.
Construction quality is another vital factor. Valves should have reliable seals and robust mechanisms. Inconsistent quality can result in premature failure. An analysis found that nearly 30% of check valve issues stem from poor manufacturing processes. Focusing on these details ensures a valve can perform under demanding conditions. Always question whether the construction meets the specific needs of your application.
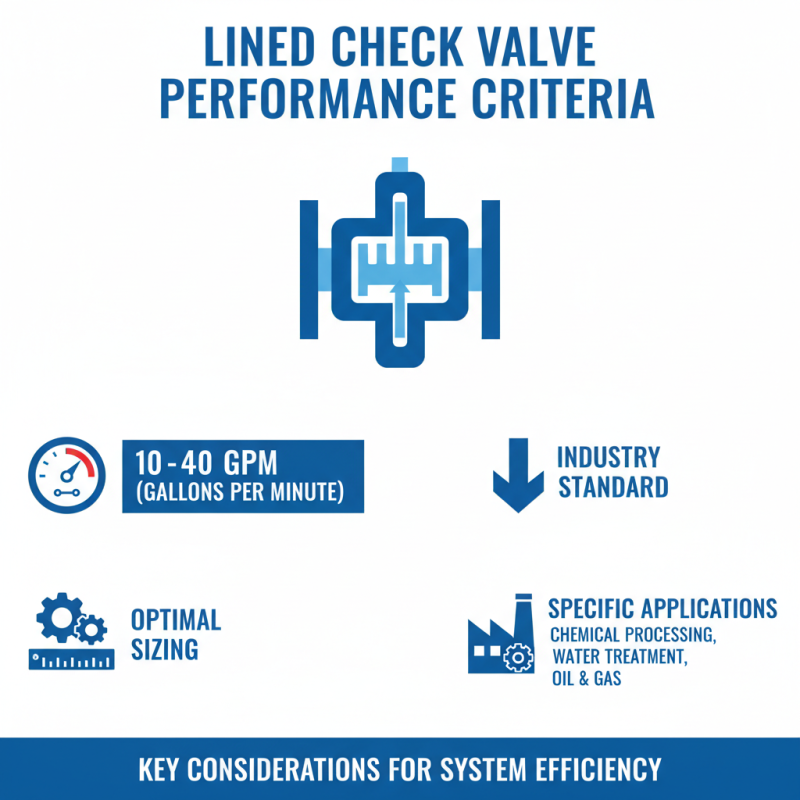
When selecting a lined check valve, performance criteria are essential. Assessing flow rates is crucial. According to industry reports, optimal flow rates can range from 10 to 40 gallons per minute. Understanding these figures helps in determining the right size and type for specific applications.
Another critical aspect is the pressure rating. Many lined check valves must withstand up to 150 PSI. If a valve's rating isn’t high enough, it could fail under pressure. The materials used in valves also influence their performance. Corrosion-resistant linings enhance durability, which is vital in harsh environments.
Users often overlook maintenance needs. A valve may perform well initially, but long-term reliability is a concern. Regular inspections are necessary, yet they are sometimes neglected. Operators should consider the lifecycle of the valve. Evaluating installation ease can save time and costs. If it doesn't fit properly, the entire system could face issues. Understanding these performance criteria is not just beneficial; it’s essential for optimal operation.
When choosing a lined check valve, considering the manufacturer's reputation is crucial. A strong reputation often indicates reliable products. Look for companies with extensive experience. Seek out feedback from previous customers. Their insights can reveal the valve's long-term performance. High-quality manufacturers typically offer better customer support and service.
Warranty options are another essential factor. A comprehensive warranty reflects a company's confidence in its product. Check what the warranty covers. Does it include parts and labor? A long warranty period can provide peace of mind. It shows that the manufacturer stands behind their products, which is important in any investment. Evaluating warranty conditions can prevent future headaches.
Take your time when making a decision. Research and compare various options. It’s easy to overlook details in a rush. Keep an eye on reviews, and ask questions. Making an informed choice protects your investment in the long run. Sometimes, a lower price may not be worth the risk of potential failures.